目标
- 浏览器路由实现的原理
- 如何实现
<route-view />组件 - 代码结构
- 实现一个简单的 DEMO
- 实现 History 和 Hash 两种模式
- push, back, replace, go, forward, back
- 支持 path 和 name 的路由跳转,支持传参
- 根据路由信息,渲染对应的组件,输出
<mock-router-view /> - 支持守卫模式
- 实现 History 和 Hash 两种模式
代码结构
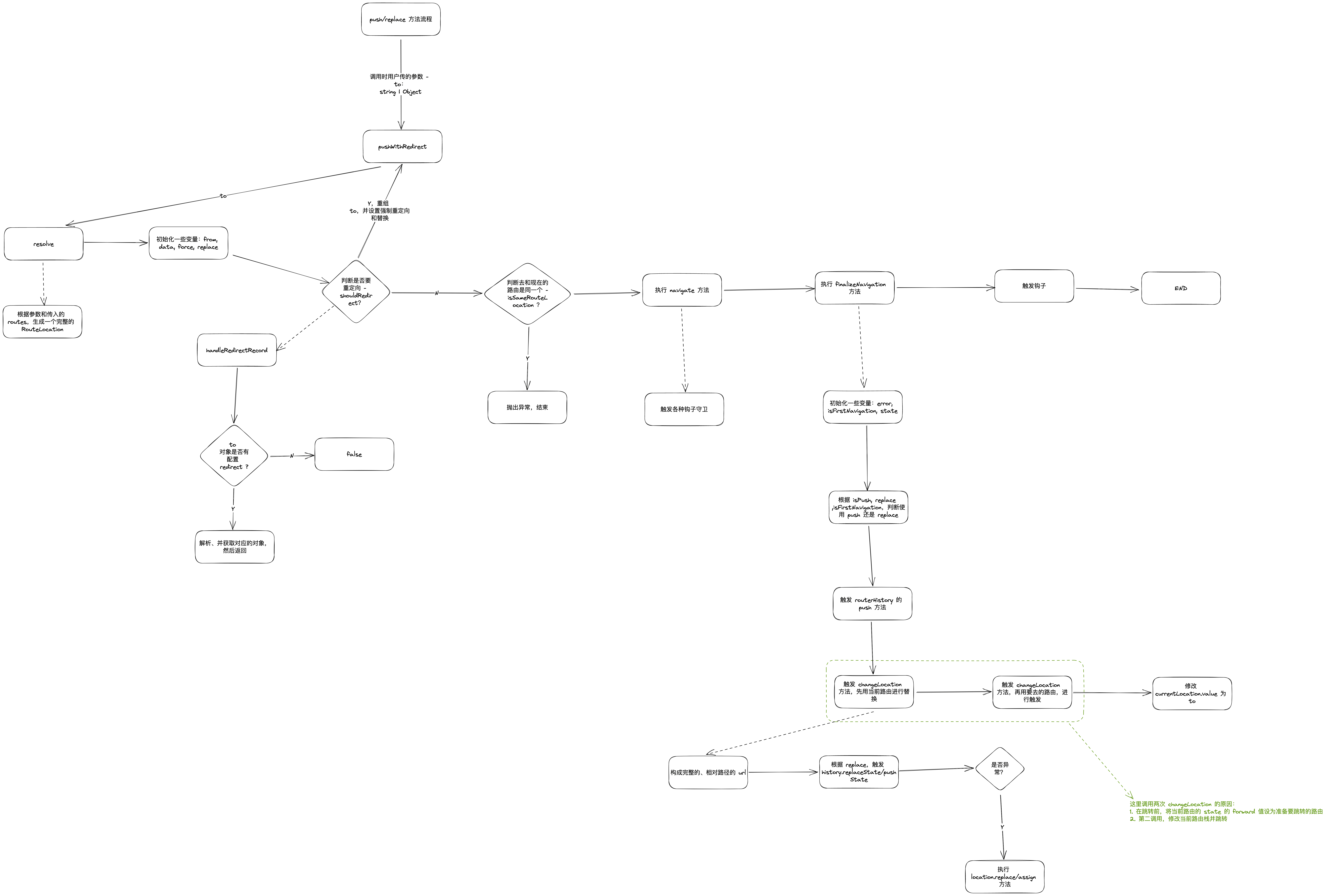
代码目录
主要看下根目录结构和 src 目录:
shell
[ 672] .
|-- [ 57K] CHANGELOG.md
|-- [ 680] SECURITY.md
|-- [ 864] __tests__
|-- [ 915] api-extractor.json
|-- [ 608] e2e
|-- [ 179] index.js
|-- [ 684] jest.config.js
|-- [6.5K] nightwatch.conf.js
|-- [3.9K] package.json
|-- [6.6K] rollup.config.mjs
|-- [ 160] size-checks
|-- [ 736] src
| |-- [9.5K] RouterLink.ts
| |-- [7.5K] RouterView.ts
| |-- [ 217] config.ts
| |-- [ 15K] devtools.ts
| |-- [4.9K] encoding.ts
| |-- [5.5K] errors.ts
| |-- [ 233] global.d.ts
| |-- [2.7K] globalExtensions.ts
| |-- [ 192] history
| | |-- [4.8K] common.ts
| | |-- [2.1K] hash.ts
| | |-- [9.8K] html5.ts
| | `-- [3.2K] memory.ts
| |-- [2.3K] index.ts
| |-- [1.5K] injectionSymbols.ts
| |-- [6.9K] location.ts
| |-- [ 224] matcher
| | |-- [ 17K] index.ts
| | |-- [1.5K] pathMatcher.ts
| | |-- [ 11K] pathParserRanker.ts
| | |-- [4.9K] pathTokenizer.ts
| | `-- [2.4K] types.ts
| |-- [ 13K] navigationGuards.ts
| |-- [4.1K] query.ts
| |-- [ 41K] router.ts
| |-- [6.3K] scrollBehavior.ts
| |-- [ 160] types
| | |-- [ 13K] index.ts
| | |-- [ 342] typeGuards.ts
| | `-- [ 762] utils.ts
| |-- [ 539] useApi.ts
| |-- [ 192] utils
| | |-- [ 60] README.md
| | |-- [ 461] callbacks.ts
| | |-- [ 55] env.ts
| | `-- [ 913] index.ts
| `-- [ 314] warning.ts
|-- [ 320] test-dts
|-- [ 672] tests_output
|-- [ 725] tsconfig.json
`-- [ 128] vetur
32 directories, 170 files路由处理流程
Vue-Router 整个路由触发的流程:
- Navigation triggered.
- Call
beforeRouteLeaveguards in deactivated components.- Call global
beforeEachguards.- Call
beforeRouteUpdateguards in reused components.- Call
beforeEnterin route configs.- Resolve async route components.
- Call
beforeRouteEnterin activated components.- Call global
beforeResolveguards.- Navigation is confirmed.
- Call global
afterEachhooks.- DOM updates triggered.
- Call callbacks passed to
nextinbeforeRouteEnterguards with instantiated instances.来源:Vue-Router 官方文档
问题
如何实现支持 hash、history 和 memory 模式?
三种模式分别使用:
- createWebHashHistory
- createWebHistory
- createMemoryHistory 来生成
history实例,并传给createRouter的history属性 三种的实现,都是基于RouterHistory的定义来实现,这样在使用history的时候不要过多地考虑什么模式要特别地处理,只关注使用即可。具体地处理分别在三个函数里面
的实现
基于 defineComponent 的函数组件:
- 提供一些依赖
- 从
matchedRoute获取到要渲染的路由组件 - 当路由信息变化时,根据相关逻辑触发
leaveGuards和updateGuards
根据 inject(routerViewLocationKey) 获取到当前 match 的路由信息,然后再根据 depth 获取到要渲染的路由组件:
typescript
// 伪代码
const injectedRoute = inject(routerViewLocationKey)!
const routeToDisplay = computed<RouteLocationNormalizedLoaded>(
() => props.route || injectedRoute.value
)
const injectedDepth = inject(viewDepthKey, 0)
cont depth = computed<number>(() => {
let initialDepth = unref(injectedDepth)
const { matched } = routeToDisplay.value
let matchedRoute: RouteLocationMatched | undefined
while (
(matchedRoute = matched[initialDepth]) &&
!matchedRoute.components
) {
initialDepth++
}
return initialDepth
})
// 当前要渲染的路由信息
const matchedRouteRef = computed<RouteLocationMatched | undefined>(
() => routeToDisplay.value.matched[depth.value]
)为什么 useRoute 和 useRouter 不能在 setup 和函数组件外使用
因为 route 和 router 需要拿到当前 Vue 的上下文。而 useRoute 等方法是基于 Vue 的 compositionAPI 的,如果不在 setup 和函数组件内使用,无法拿到当前 Vue 实例的上下文
什么情况会触发 popState 事件
- 用户点击浏览器的前进或后退按钮。
- 使用 JavaScript 中的
history.back()、history.forward()或history.go()方法导航历史记录。 - 使用 JavaScript 中的
history.pushState()或history.replaceState()方法改变历史记录,但请注意,这两个方法本身不会触发popstate事件。只有当用户在由这些方法创建的历史记录条目之间导航时,才会触发popstate事件。
其他
利用 pushState 和 replaceState 不会触发 popState 事件的特点,在 push 的前,先将当前 路由 state 的 forward 设为要去的路由,并使用 history.replaceState 替换,然后才使用 pushState 进行跳转。
然后当用户后退,再前进的时候,就能获取到要前进的 state 是什么
DEMO
结构: 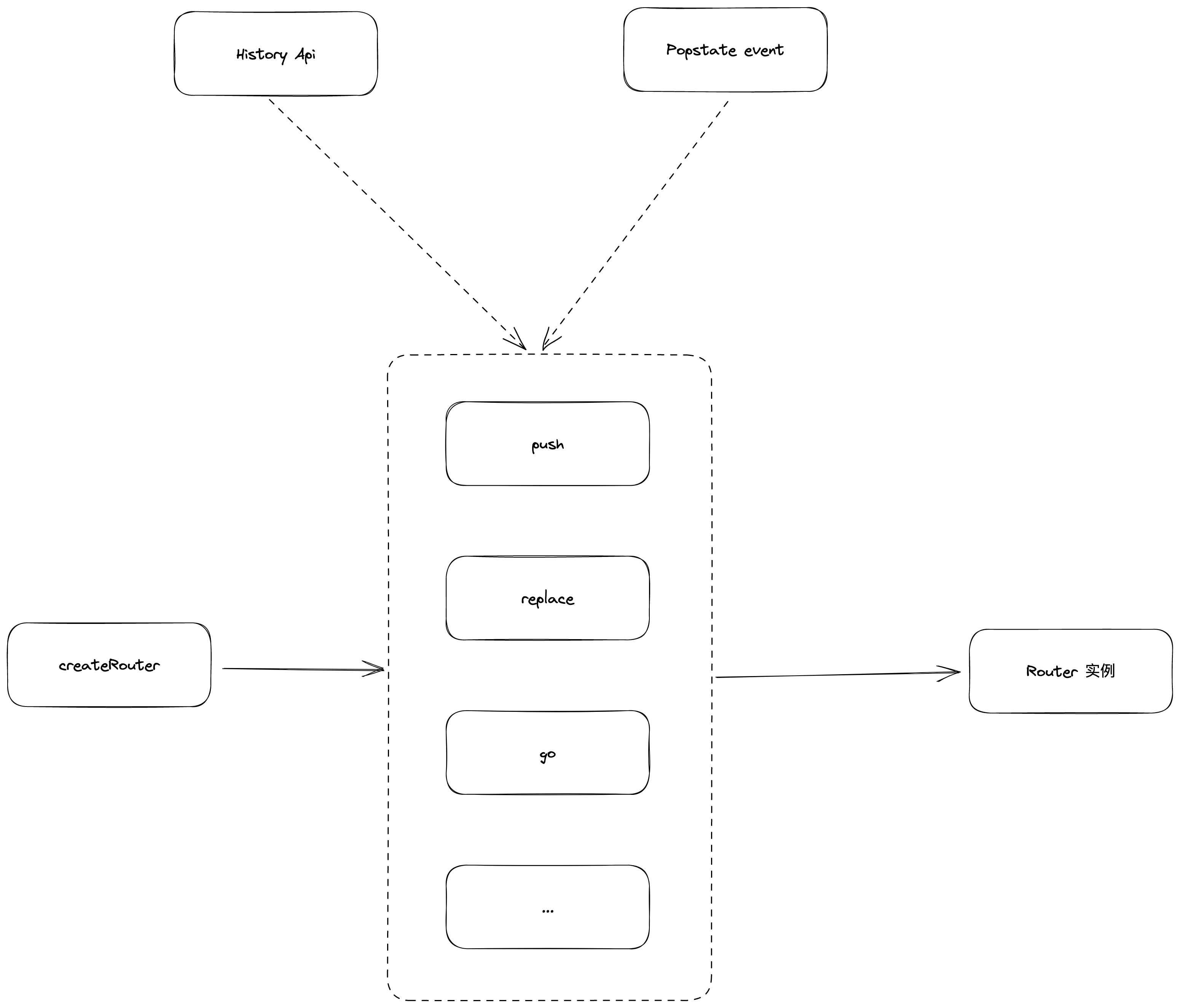
路由执行的流程: 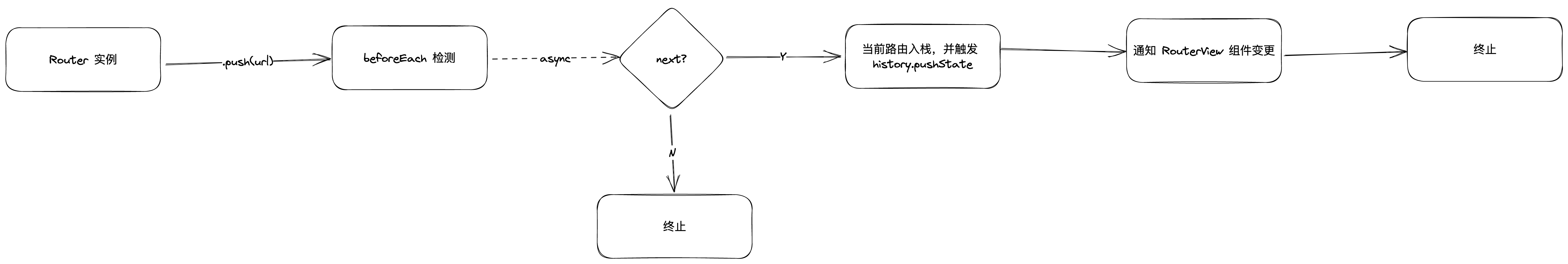
第一版
简单实现了以下功能:
- 基于 history 模式,实现 push, replace, go, back, beforeEach 等方法和钩子
- 实现
router-view组件,基于配置和当前 URL 信息,选项渲染对应的组件
存在的问题:
- 当前的 beforeEach 的实现,是根据缓存的路由栈去获取 from 信息,再判断是否通过,这样可以在 URL 变化前做操作。但首次进入页面后,触发 go 和 back 方法时,beforeEach 的钩子参数会获取不了
mock-router:
typescript
import { h, reactive, ref } from "vue"
import { observer } from "../utils"
type TQuery = Record<string, string>
export interface IRouteItem {
path: string
query: TQuery
component: any
children: IRouteItem[]
}
export interface MRouterOptions {
mode: 'hash' | 'history'
routes: IRouteItem[]
}
type TBeforeEach = (to: IStackItem, from: IStackItem, next: (val: boolean) => void) => void
export interface IRouter {
push: (path: string, query?: TQuery) => void
replace: (path: string, query?: TQuery) => void
go: (number: number) => void
back: () => void
beforeEach?: TBeforeEach
afterEach?: (to: IStackItem, from: IStackItem) => void
setBeforeEach: (b: TBeforeEach) => void
}
export interface IStackItem {
path: string
query?: TQuery
}
class Stack {
data: IStackItem[] = []
cb = (data: IStackItem) => {}
constructor(pCb: (data: IStackItem) => void) {
this.cb = pCb
}
add(data: IStackItem) {
this.data.unshift(data)
this.cb(data)
}
replace(data: IStackItem) {
this.data.shift()
this.add(data)
this.cb(data)
}
shift() {
if (!this.data.length) return
const data = this.data.shift()
if (data) this.cb(data)
return data
}
getCurrent() {
return this.data[0]
}
getPrev() {
return this.data[1]
}
}
const getPathWithQuery = (path: string, query?: TQuery) => {
// const url = new URL(path);
let url = ''
if (path.includes('?')) {
url = path + '?'
} else {
url = path
}
return url + Object.values(query ?? {}).map(([k, v]) => {
return `${k}=${v}`
}).join('&')
}
export const createRouter = (options: MRouterOptions): IRouter => {
let beforeEach: IRouter['beforeEach'] = (to, from, next) => next(true)
let afterEach: IRouter['afterEach'] = (to, from) => {}
const currentState = ref<IStackItem>({
path: '',
query: {}
})
function getCurrentState() {
if (history.state) return history.state
const { pathname } = location
return options.routes.find(v => v.path === pathname)
}
function getComponentByPath(path: string) {
const route = options.routes.find(v => v.path === path)
return route
}
const stack = new Stack((data) => {
currentState.value.query = data.query
currentState.value.path = data.path
const route = getComponentByPath(data.path)
if (route) {
observer.dispatch('change', route.component)
}
})
const checkBeforeEach = (to: IStackItem, from: IStackItem) => {
return new Promise(resolve => {
if (beforeEach) {
beforeEach(to, from, (next: boolean) => {
resolve(next)
})
}
})
}
let isGo = true
const push = async (path: string, query?: TQuery) => {
const to = {
path, query
}
const next = await checkBeforeEach(to, stack.getCurrent())
console.log('next', next);
if (!next) return
history.pushState(to, '', getPathWithQuery(path, query))
stack.add({ path, query })
}
const replace = async (path: string, query?: TQuery) => {
const to = {
path, query
}
const next = await checkBeforeEach(to, stack.getCurrent())
if (!next) return
history.replaceState(to, '', getPathWithQuery(path, query))
stack.replace({ path, query })
}
const go = (number: number) => {
// TODO
isGo = true
history.go(number)
}
const back = async () => {
const next = await checkBeforeEach(stack.getPrev(), stack.getCurrent())
if (!next) return
isGo = false
history.back()
}
window.addEventListener("popstate", (event) => {
console.log(
`location: ${document.location}, state: `,
event.state
);
if (isGo) {
stack.add(event.state)
} else {
stack.shift()
}
});
setTimeout(() => {
stack.add(getCurrentState())
}, 0);
const router = {
push,
replace,
go,
back,
beforeEach,
afterEach,
setBeforeEach: (b: IRouter['beforeEach']) => {
beforeEach = b
}
}
return router
}mock-router-view
vue
<template>
<component v-if="state.component" :is="state.component" />
</template>
<script lang="ts">
export default { name: 'RouterView' }
</script>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
import { observer } from "../utils"
const state = reactive<{ component: any }>({
component: undefined
})
console.log('init');
const sub = observer.createSubscriber()
sub.addListener('change', (com: any) => {
console.log('change component', com);
state.component = com
})
</script>chatGPT 生成的 Hash 模式的路由
typescript
class HashRouter {
constructor() {
// 初始化时,监听 hashchange 事件
window.addEventListener('hashchange', this.onHashChange);
}
// 更新 hash
public navigate(hash: string): void {
window.location.hash = hash;
}
// 处理 hash 变化
private onHashChange = (): void => {
const currentHash = window.location.hash;
console.log('Hash changed:', currentHash);
// 在这里执行你的导航逻辑,例如更新页面内容或改变页面状态
};
}
// 使用 HashRouter
const router = new HashRouter();
// 导航到一个新的 hash
router.navigate('#/example');